Nourishing Balance: Exploring Diet and Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases through Ayurveda
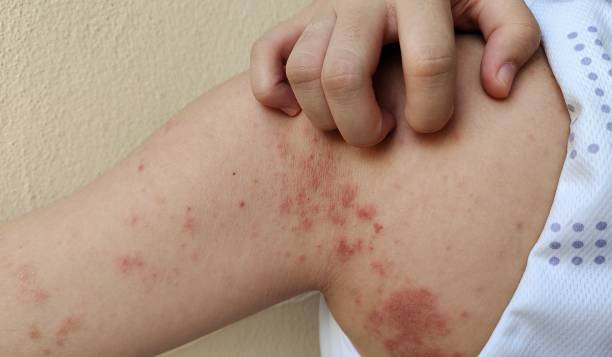
Inflammatory expressions: redness, heat, swelling, pain, & loss of function.
Introduction: Inflammatory Autoimmune diseases pose a formidable challenge, as the body's immune system misguidedly attacks its tissues, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and organ malfunction. Identifying early signs and symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. From notable skin changes like rosacea in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) to the painful burning sensations of gouty arthritis, understanding these indicators is paramount in navigating the complexities of autoimmune diseases.
A Holistic Approach to Management: The management of autoimmune diseases necessitates a holistic approach that spans various medical specialties. Rheumatology, immunology, and dermatology often collaborate to deliver tailored care. With early detection and appropriate treatment, individuals grappling with autoimmune diseases can carve out fulfilling lives.
Ayurveda's Dietary Wisdom: Within Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of medicine, diet is central to preserving health. Fundamental to Ayurvedic tenets is the concept of "Agni," or metabolism, which can exist in a state of equilibrium or imbalance. When catabolism surpasses anabolism, precipitating cellular destruction and immune disturbances, Ayurveda refers to this state as "Tikshnagni."
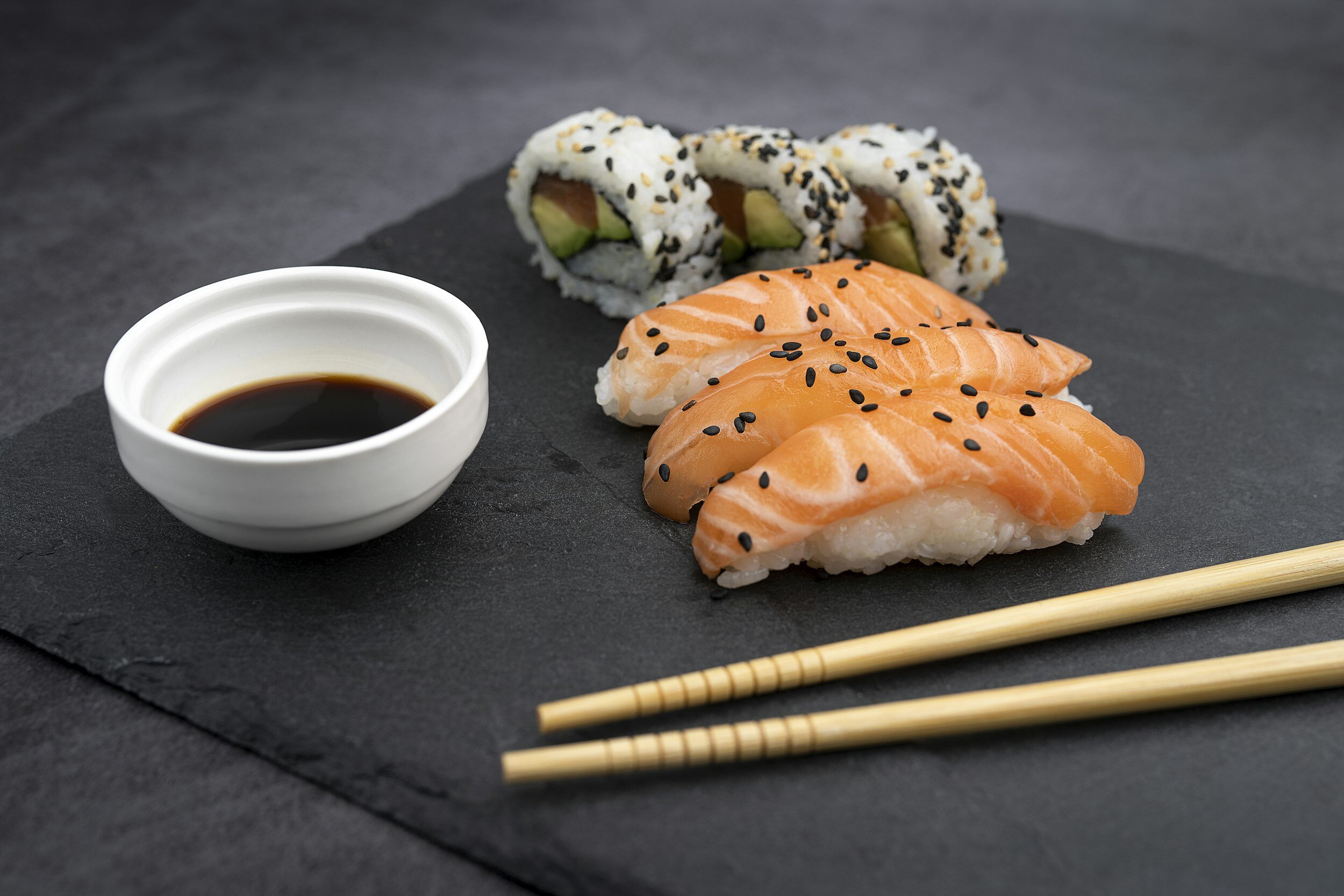
Raw fish, sour and salty foods aggravate the fire qualities.
This leads to inflammatory conditions in high pitta personalities.
Fermented and salted foods:
These are considered good appetizers, and people with low digestive fire (Agni) find them very helpful, but for those who are disturbed with Pitta, these will aggravate the inflammatory process.
Navigating Dietary Choices: Comprehending the dietary ramifications of autoimmune diseases entails recognizing how certain foods may exacerbate symptoms. While brimming with probiotics, fermented delicacies like overnight oats, kimchi, and yogurt may inadvertently amplify "Tikshnagni" in individuals grappling with autoimmune conditions. Similarly, indulging in hot, spicy fare and purine-rich components like raw fish and red meat can further stoke immune dysregulation and inflammation.
Mindful Consumption for Balance: While fermented and spicy foods boast potential health perks, exercising moderation is imperative, particularly for those managing autoimmune diseases. Striking a balance between nutritional requirements and dietary restrictions can help mitigate the risk of symptom exacerbation. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or Ayurvedic practitioners can provide personalized insights into crafting a diet that fosters overall well-being.
Conclusion: The interplay between diet and autoimmune diseases is intricate and nuanced. By embracing Ayurvedic principles and practicing mindful consumption, individuals can empower themselves to make informed dietary decisions that foster balance and assuage symptoms. Armed with awareness, adaptability, and collaborative efforts with healthcare providers, traversing the dietary terrain of autoimmune diseases transforms into a voyage of nourishment and restoration.